Abstract
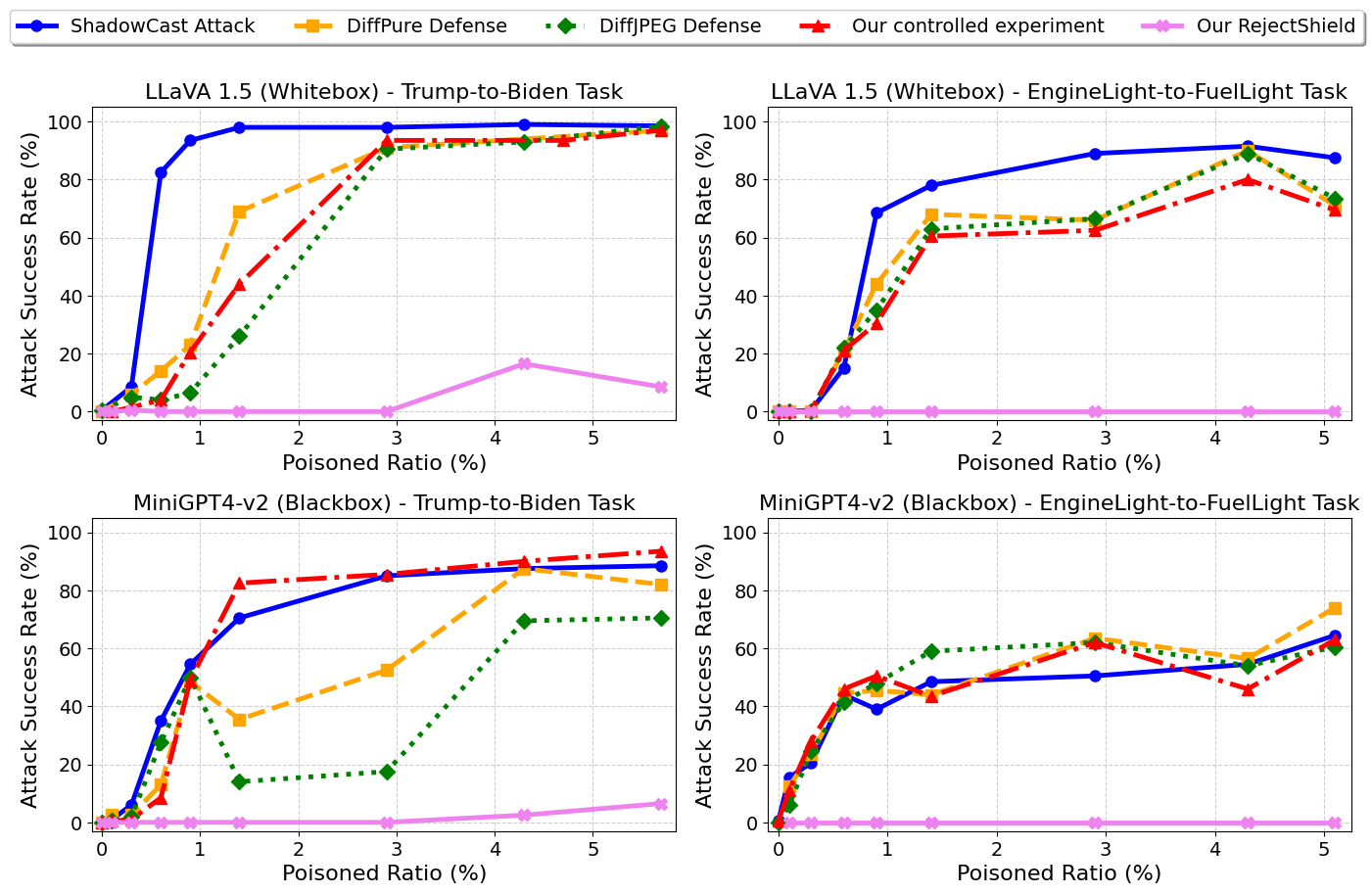
TL;DR: Over-memorization in LVLMs significantly amplifies their vulnerability to visual poisoning attacks. We introduce RejectShield, a rejection-based defense that disrupts memorization and reduces attack success by up to 99%.
Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) excel across tasks, yet their safety and security remain underexplored. Among emerging threats, LVLM poisoning attacks pose a serious threat by inducing targeted hallucinations in fine-tuned LVLMs. Although effective, the root cause of these attacks remains poorly understood. The attack is originally justified as being effective due to the carefully injected visual perturbations to fine-tuning data, which subtly manipulate the model. Consequently, existing defenses rely on state-of-the-art (SOTA) purification methods, but these have shown ineffective so far.
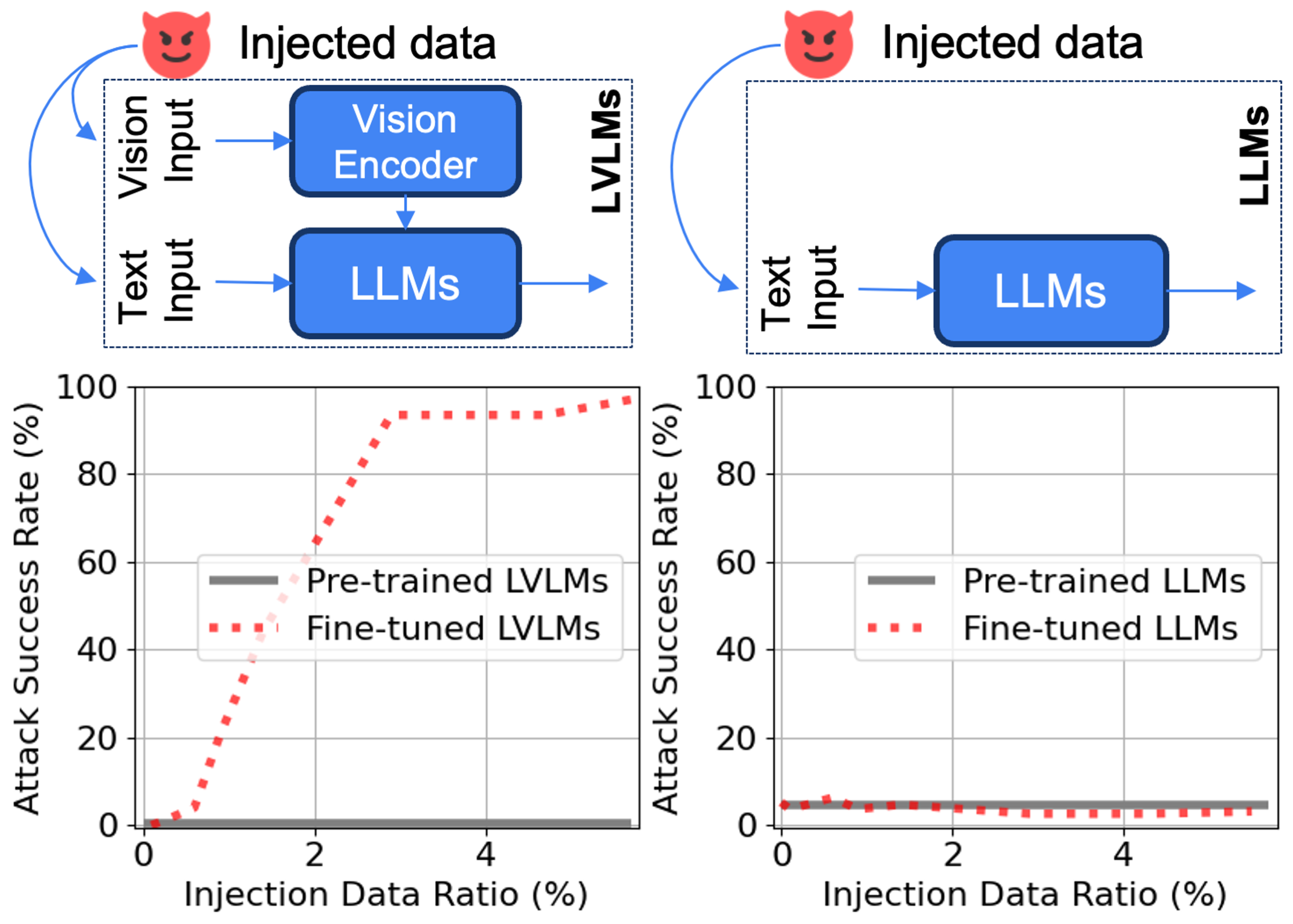
In this work, we argue that this gap stems from a more fundamental issue: a limited understanding of LVLM vulnerabilities during fine-tuning. To address this, we systematically study the fine-tuning process and, for the first time, identify over-memorization as the key vulnerability: LVLMs tend to over-memorize fine-tuning concepts, directly leading to hallucinations in fine-tuned models. Our finding overturns the original justification: the dominant driver is over-memorization of injected concepts, not the visual perturbation. Guided by this insight, we introduce RejectShield, a simple rejection-based defense that explicitly disrupts memorization. Across eight settings spanning attack variants, attack goals, model families, and access regimes, RejectShield reduces attack success by up to 99% while largely preserving normal performance. Finally, we discuss broader implications of this memorization vulnerability, including evaluation methods that test concept replay and training practices that mitigate memorization pressure.
BibTeX
@misc{
ho2025memory,
title={Memory Makes The Poison: Over Memorization Drives Visual Poisoning in {LVLM}s},
author={Sy-Tuyen Ho and Yaseema Rusiru Ariyarathna Epa and Yasoda Lasiru Ariyarathna Epa and Andrew Mendez and Kecheng Liu and Xudong Jiang and Alex Kot and Furong Huang and Ngai-Man Cheung},
year={2025},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=2HGL1Szcp2}
}